Week 1
Machine Learning and Limitations
Question 1
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is only concerned with the designing and building of intelligent agents that receive precepts from the environment and discover patterns in that environment.
- True
- False
- Regression
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- True
- False
- True
- False
- Robust
- Efficiency
- Ethical
- Lawful
Embedded Machine Learning
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
Data Collection
- Validation set
- Test set
- Common set
- Training set
- Test set
- Training set
- Validation set
- Common set
- Common set
- Training set
- Test set
- Validation set
- True
- False
- A dataset where the input dimensions of the model are equal to the output dimensions.
- A dataset that contains approximately equal number of samples in the training, validation, and test sets.
- A dataset that contains samples with the same number of dimensions.
- A dataset that contains approximately equal number of samples in each class.
Feature Extraction
- A measurable property of something that’s observed
- A plot of the data over time
- A spectral analysis used to break apart the data into its various frequency components
- A description of the overall shape and trends in the data
- True
- False
- Automatically updating a model’s parameters with data
- Analyzing the data to determine which features to use
- Reducing the number of dimensions in features to reduce computational complexity.
- Using a trained model to make predictions with unseen data
- True
- False
- True
- False
Machine Learning Overview
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- Detecting anomalies in an online banking application
- Detecting anomalies in the servomotor of a satellite
- Performing an action based on a spoken keyword
- Identifying objects in an image
- True
- False
- True
- False
- How long to train the model
- Raw data value
- The root mean square (RMS) value of all the data
- Prominent frequency values found in the data
- True
- False
- True
- False
Week 2
Neural Networks and Training
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- An iteration
- A mini-batch
- Regression
- An epoch
Evaluation, Underfitting, and Overfitting
- The model’s input dimensions do not match the data’s dimensions
- The model has underfit to the training data
- The model has overfit to the training data
- The model model has a good fit with the training data
- Add regularization terms
- Early stopping
- Use a more complex model
- Gather more data
Deploy Model to Embedded System
Question 1
- True
- False
- 1
- 3
- 5
- 10
- True
- False
- True
- False
Anomaly Detection
- True
- False
Motion Classification and Anomaly Detection
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
Question 4
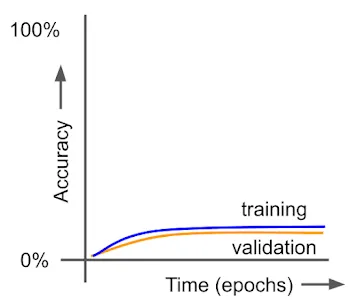
- The model has overfit to the training data
- The model has a good fit with the training data
- The model’s input dimensions do not match the data’s dimensions
- The model has underfit to the training data
- 12
- 1
- 3
- 10
- Sum the results, which will give you an index to the array of class labels
- Choose the class with the highest output value
- Average the results together, which will give you an index to the array of class labels
- Choose the class with the lowest output value
- True
- False
-
- True
- False
Week 3
Audio Classification and Sampling Audio Signals
- Translating handwriting to computer-encoded text
- Tracking wildlife
- Identifying anomalous noises in a home or office
- Translating spoken words to computer-encoded text
- 44.1 kHz
- 48 kHz
- 8 kHz
- 16 kHz
- True
- False
MFCCs and CNNs
- 20 kHz
- 10 kHz
- 5 kHz
- 40 kHz
- They provide data augmentation to help create a more robust audio classifier.
- They mimic how the human ear perceives sound.
- They mimic how the human vocal cords and mouth produce sound.
- They help prevent overfitting.
- It prevents a random selection of outputs of the previous layer from reaching the next layer.
- It combines the outputs of the previous layer such that they each have a value between 0 and 1 and all sum to 1.
- It filters the image using a kernel.
- It slides a window over the image, selecting the highest pixel value in that window.
- True
- False
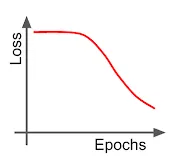
- Not enough training time
- Overfit model
- Underfit model
- Too much training time
Implementation Strategies
- Choose the class with probability over a threshold
- Sum the probabilities together and divide by 4
- Choose the class with the lowest probability score
- Choose the class with the highest probability score
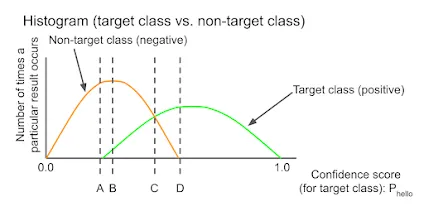
- A
- B
- C
- D
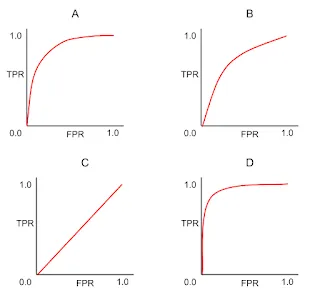
- A
- B
- C
- D
- True
- False
- True
- False
Implementation Strategies
- True
- False
- 16 kHz
- 4 kHz
- 8 kHz
- 32 kHz
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
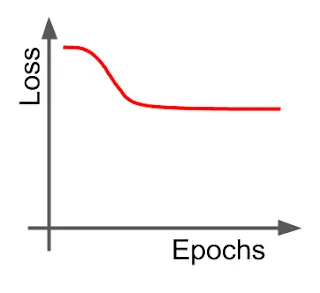
- Increase model complexity
- Gather more data
- Train for longer
- Early stopping
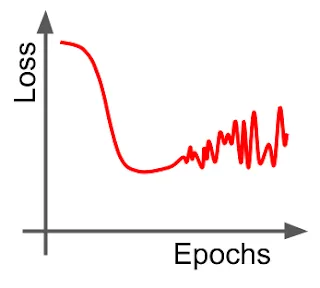
- Overfit model
- Underfit model
- Learning rate is too low
- Learning rate is too high
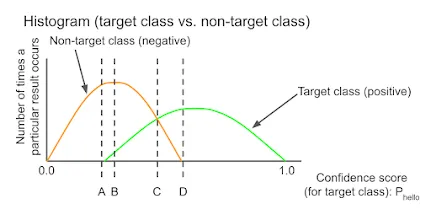
- A
- B
- C
- D
- True
- False